Drill Collar Weight Calculation Method
Drill Collar Weight Calculation is not difficult to run. Basically there are two methods for such calculations. In this article we will discuss both methods and the difference between them. This article is to provide a full guide for Drill Collars Size & Weight Selection.
Buoyancy Factor Method
Before going deep in that drill collar weight calculation methods, please consider the following notes:
Ensures that buckling is restricted to the Drill Collars and no buckling occurs in the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipes above the Drill Collars.
The required Collar length to provide a desired weight on the Drilling Bit can be calculated as follows.
Lc=WOB*SF/BF*Wc*Cosθ
Where,
WOB = desired weight on bit, lb
SF= safety factor (1.1-1.15),
BF= buoyancy factor,
Wc= drill collar weight in air, lb/ft
I = maximum hole angle at BHA, degrees
This method does not take into account the hydraulic forces acting on the bottom end of the Drill Collars and on the shoulder areas between Drill Collars and the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipes.
You must understand that the Drill Collars length calculated by previous equation is not enough to provide all the desired weight on the Drilling Bit, and, therefore, the remainder of the weight will be provided by heavy weight drill pipe (HWDP) or drill pipes above the drill collars.
Drill Pipe Buckling
Drill Pipe Buckling is a problem that must be avoided at all times. Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe Buckling induces stresses in the pipe which will cause premature pipe fatigue and pipe failure.
The Drill String Buckling Neutral Point(BNP)
Lubinski defined The Buckling Neutral Point as the point in the Drill Collar string below which the pipe is buckled (under compression) or will have a tendency to buckle, and above (also under compression) which no buckling will occur. The buckling neutral point is calculated by the following equation.
BNP= WOB /BF*Wc
Above Equation states that no buckling occurs above the drill collars as long as the weight on the Drilling Bit does not exceed the buoyed weight of the Drill Collar.
The Drill String Axial Stress Neutral Point
In some cases it may be necessary to calculate the axial stress in the Drill String or locate the axial stress neutral point. When axial stress must be determined, all forces acting on the Drilling Bottom Hole Assembly BHA must be considered including the hydrostatic forces.
The hydraulic forces are a result of the hydrostatic pressure of the mud and are computed by multiplying the hydrostatic pressure times the respective section area.
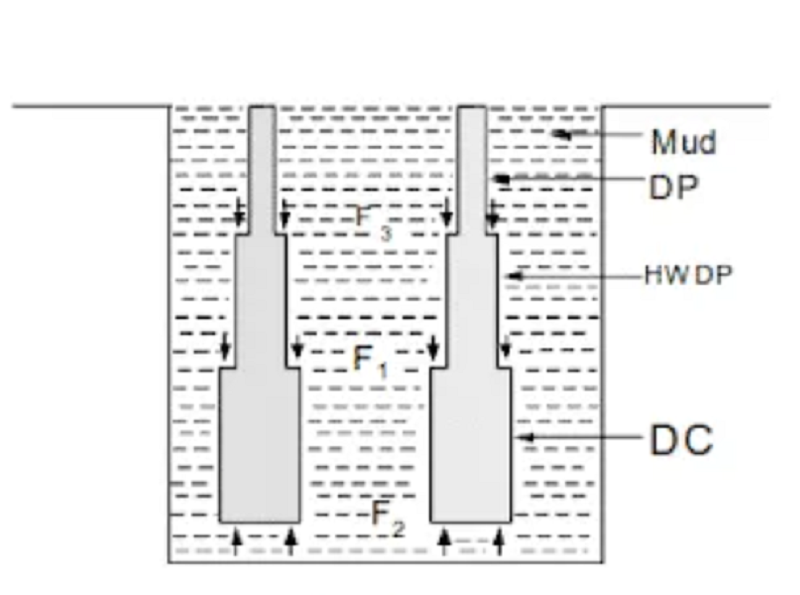
Drill Collar Calculation Pressure Area Method Conclusion
The number of Drill Collars calculated by the Buoyancy Factor method is not enough to provide all the weight on the Drilling Bit WOB. Some of the WOB will be provided by the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe directly above the Drill Collars. For this reason the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe above the Drill Collars will be in compression but not buckled. It is an acceptable practice to use Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe in compression as long as it is not buckled.
The buckling neutral point is always near the top of the Drill Collars. The Drill Collars below the neutral point will have a tendency to buckle. The Drill Collars and Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) above the neutral point will not buckle as long as the actual weight applied on the Drilling Bit while drilling does not exceed the WOB used in the calculations. If the actual WOB exceeds the WOB used in the calculations then the number of Drill Collars must be increased, otherwise, the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe above the drill collars will buckle. Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) or Drill Pipe should never be used in a buckled condition.
Buoyancy Factor Method vs Pressure Area Method
Comparison between the Buoyancy Factor Method and the Pressure Area Method for the Drill Collar weight calculations.
It can be seen that the Drill Collar length calculated by the Pressure Area Method is almost twice that calculated by the Buoyancy Factor Method and, therefore, is enough to provide all the Weight on Drilling Bit WOB.
For this reason, In Pressure Area Method only the Drill Collar
are in compression while the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe HWDP is in tension.
The buckling neutral point is the same in both cases.
Either of the two methods can be used to calculate the length of the Drill Collar
However, the Pressure Area Method has the following disadvantages:
Requires more Drill Collar to keep the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe HWDP or Drill Pipes in tension. This serves no useful purpose because whether the pipe above the buckling neutral point is in tension or compression is irrelevant to fatigue damage, if the pipe is not buckled.
The need to procure, transport, maintain, inspect and handle the extra Drill Collar increases the cost of the drilling operation (check also drilling cost per foot).
Adding more Drill Collars increases the weight of the Drill String and the tensile stress in the Drill Pipes at all depths. The increase in stress will increase the rate of fatigue attack and reduce the life of the Drill Pipes.




